ENG 004 Lecture 3, Oct 4, 2012
Announcements
- Studios start today!
- Bring Sketchbooks to studio!
- Lecture HW #1 due Tuesday
- Wait listed students please be a patient
- Read Chapter #2
Topics
Visual Culture/Thinking: Seeing, Imagining, Drawing/Sketching,
Diagramming, Environment, Culture
Graphics in Design: Visualization, Communication, Documentation
Sketches vs Drawings
Conventions
Visual Thinking
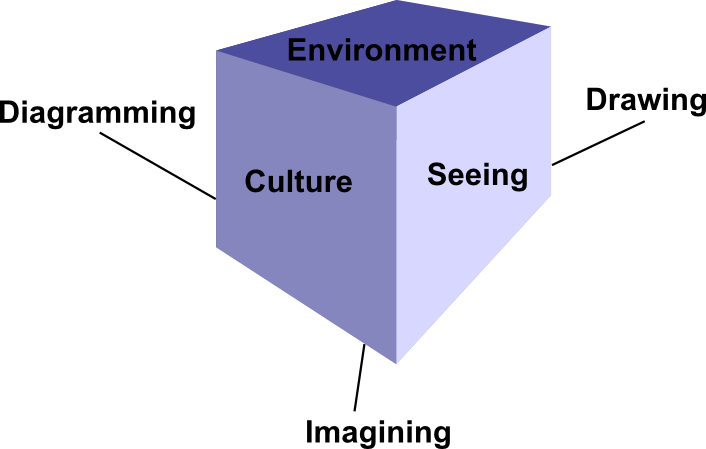
Environment
Physical Workspace to encourage visual ability:
- Lighting
- Surface to work on
- Sound/music/silence
- Art/models/mobiles/etc
Looking for inspiration
Culture
Understanding visualization culture and the tools to do so
The way we relate to others:
- Brainstorming
- Sketching
- Idea logs, Sketchbooks
- Physical Design, Prototypes
- Critiquing
Seeing
Visual exercises to stretch your visual ability.
Tune-up your seeing skills
- Be aware of how you see
- Unblock you visual stereotypes
- Translate motion into form
- Notice detail
- Sort, categorize, and group elements
- View from other's perspectives
Drawing/Sketching
Does not require and artistic ability. It is a skill.
Enlivens the imagination
- Used to enhance seeing
- Use basic techniques: shading, perspective, etc
- Learn how to create basic objects and shapes
Diagramming
- Make the abstract concrete
- Pictorial conversation to describe and illustrate ideas
- Use symbols
- Flow charts, free body diagrams, Sankey diagrams, Venn diagrams,
etc
Imagining
- Enhance inner visualization
- Using mental imagery to generate ideas
- Recognize your own imaginative abilities
- Use words, sounds, images to articulate ideas
Role of Graphics in Design
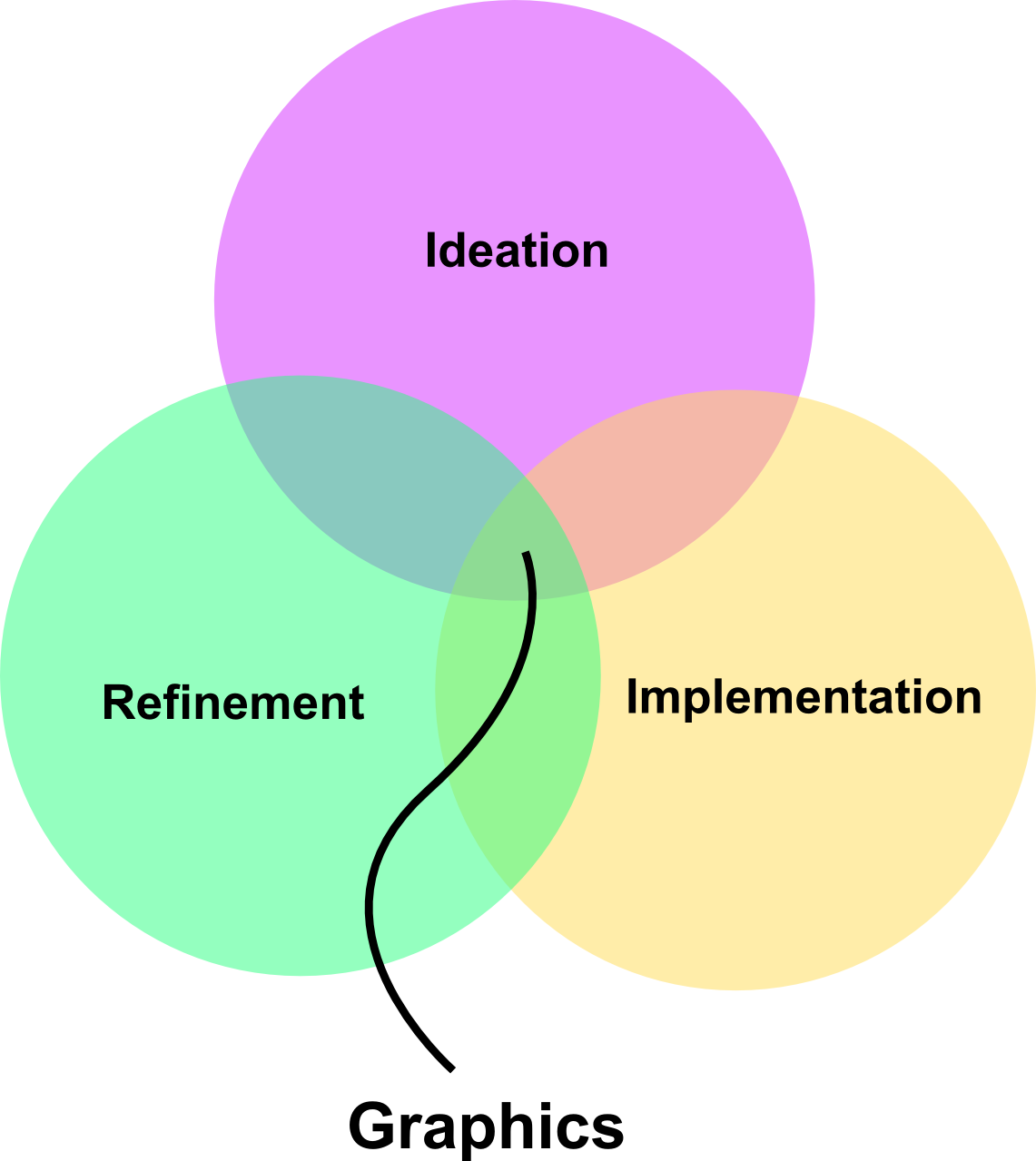
Role of Graphics in Design
Visualization
Communication
Documentation
Visualization
The ability to see objects in your mind
- Mentally seeing things that don't exist or that need modification
- Sketches are the first physical capture of your mental image
- Mentally fly through of objects
- Ability to see relative motion
Communication
Refine drawings and models to improve communication of ideas
Assist others to visualize what you see
Clear way to relay information to others
Documentation
Create a permanent record of a design
Detailed 2D/3D drawings
Contains all information needed to create/use objects
Provides communication for manufacturing, service, sales, etc
Sketching Vs Drawing

Sketching Vs Drawing
Sketching
Transferring of ideas or concepts onto paper or in a computer to
quickly capture them graphically.
Drawing
Transferring of an object's shape, size, proportion and/or main
features onto paper or computer.
http://ikastika.files.wordpress.com/2008/10/elephant-sketch500.jpg
Contour Sketch
Emphasize mass and volume rather than detail.
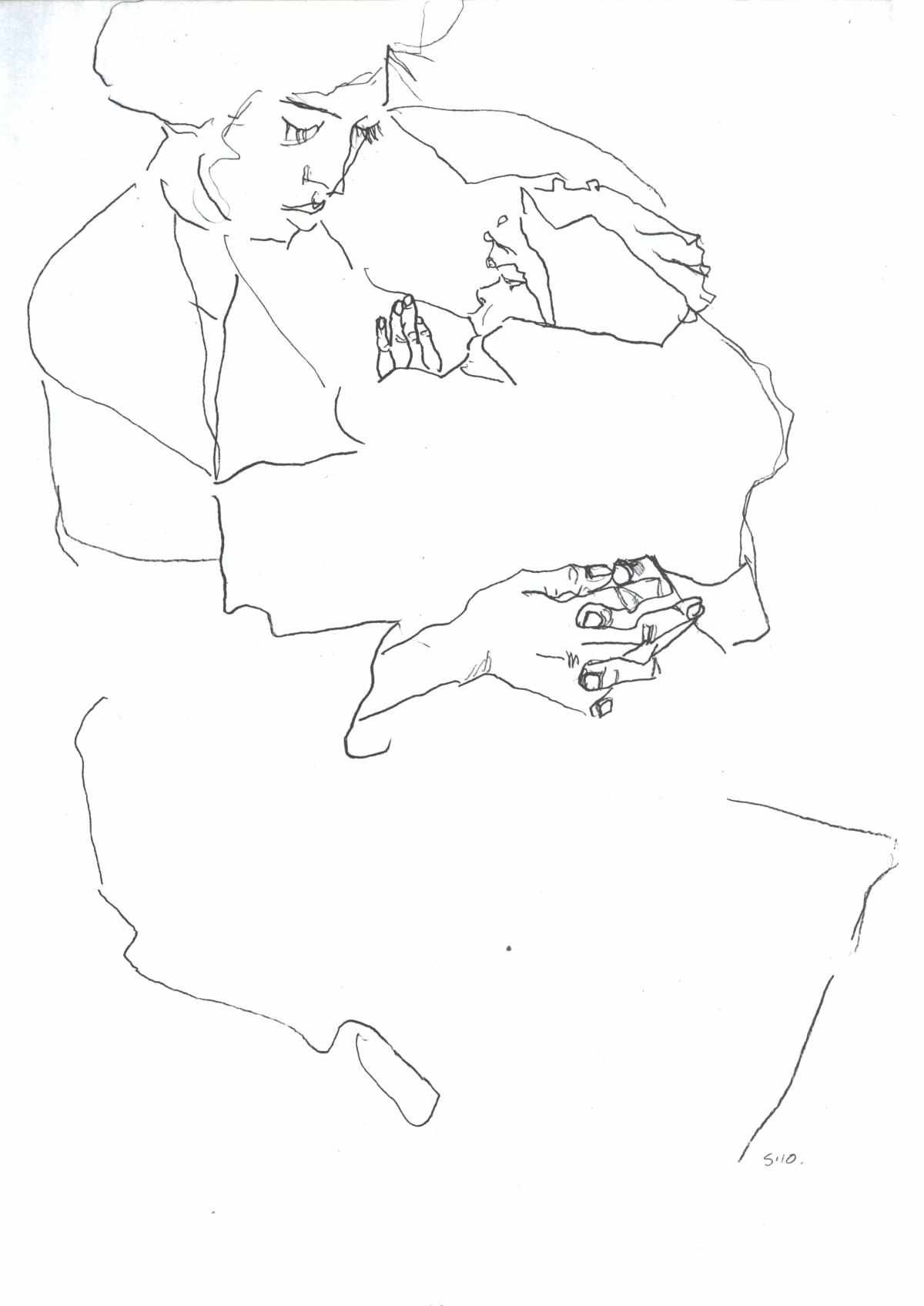
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Schiele_-_Mutter_mit_Kind_-_1910.jpg
Technical Drawing
Emphasize technical details
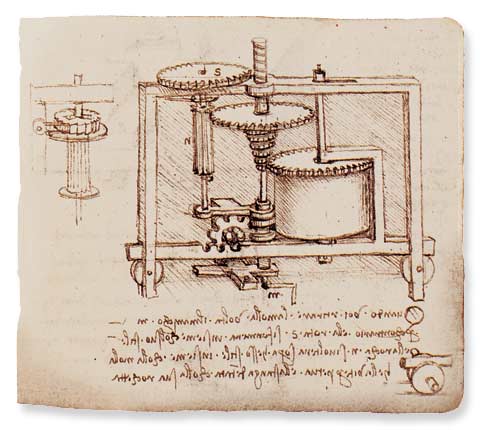
http://www.odec.ca/projects/2007/viva7s2/DaVinci_CVP_illustration.jpg
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Design_for_a_Flying_Machine.jpg
Design Standards and Conventions
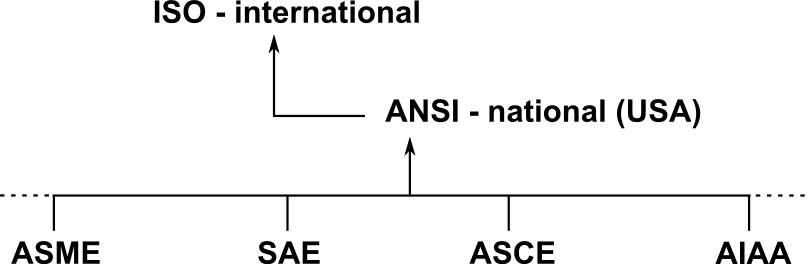
ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
- Governing body in the United States that generates and publishes
standards and conventions for science, technology, and engineering.
- NGO (non-governmental organization) comprised of professionals from
various technical fields.
ISO (International Standards Organization)
The ISO is a standards body for the global level
Line Types
See Chapter 5 page 232
- Construction lines: light, erasable guide lines used to start
sketches
- Center Line: indicates symmetry, paths of motion, centers of circles or
circular arcs.
- Break Line: shows where an object is broken to reveal the interior or
to save drawing space. Two forms: freehand thick line and long ruled think
line with zig zags.
- Dimension, extension, and leader lines: used to indicate the size of
location of a feature
- Section lines: represents surfaces cut by the cutting plane
- Cutting Plane lines: show the locations of the cutting plane
- Visible lines (object lines): shows features visible in the current
projection
- Hidden lines: represents features that cannot be seen in the current
projection
- Phantom lines: are used to represent a movable feature in its different
positions.
- Stitch lines: are used to indicate a sewing or stitching process.
- Chain lines: are used to indicate that a surface is to receive
additional treatment.
- Symmetry lines are used as an axis of symmetry for a particular
view
Proportions and Construction Lines
 ←
→
←
→
/
#