Legibility/Communication

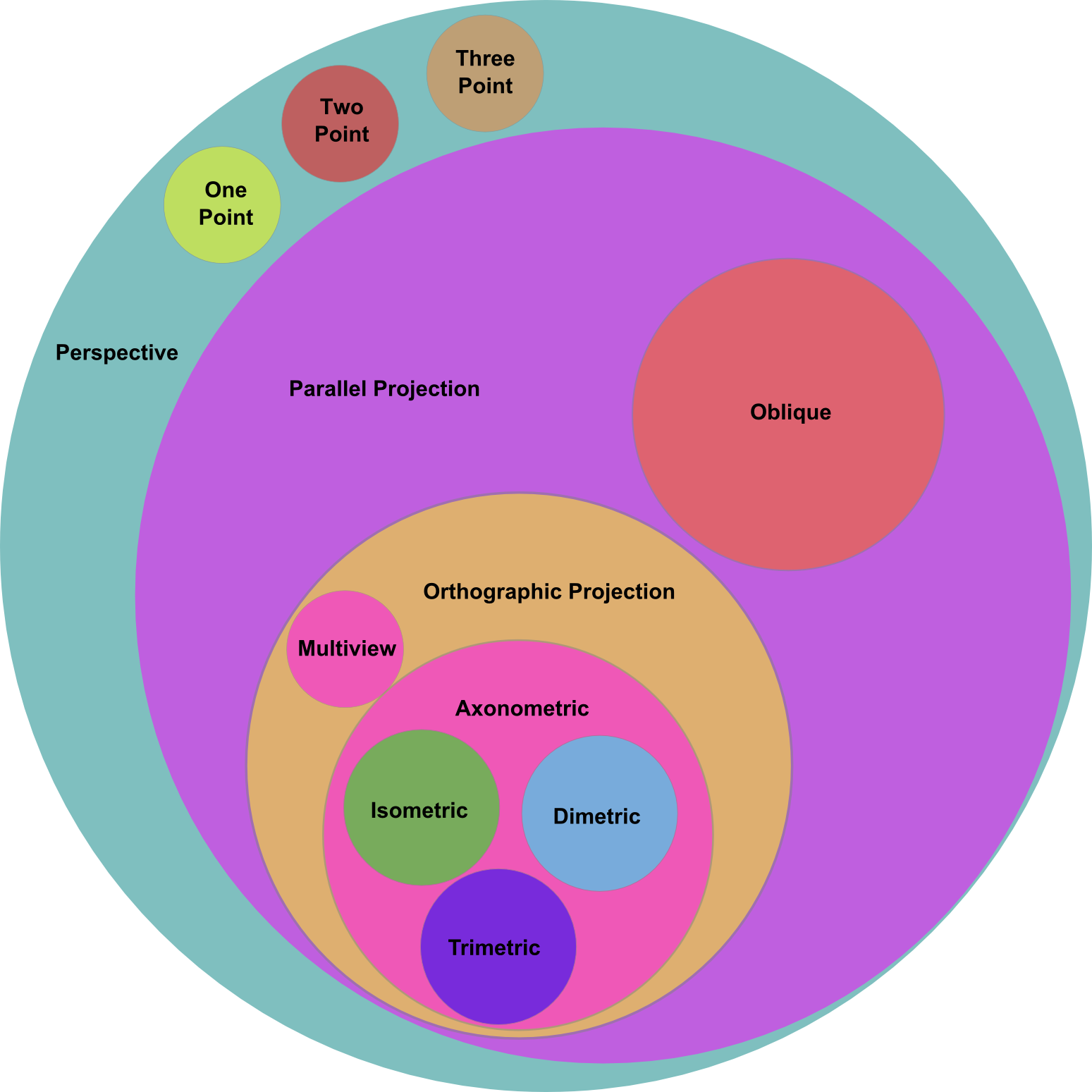
Drawing Types
3D to 2D, 2D to 3D
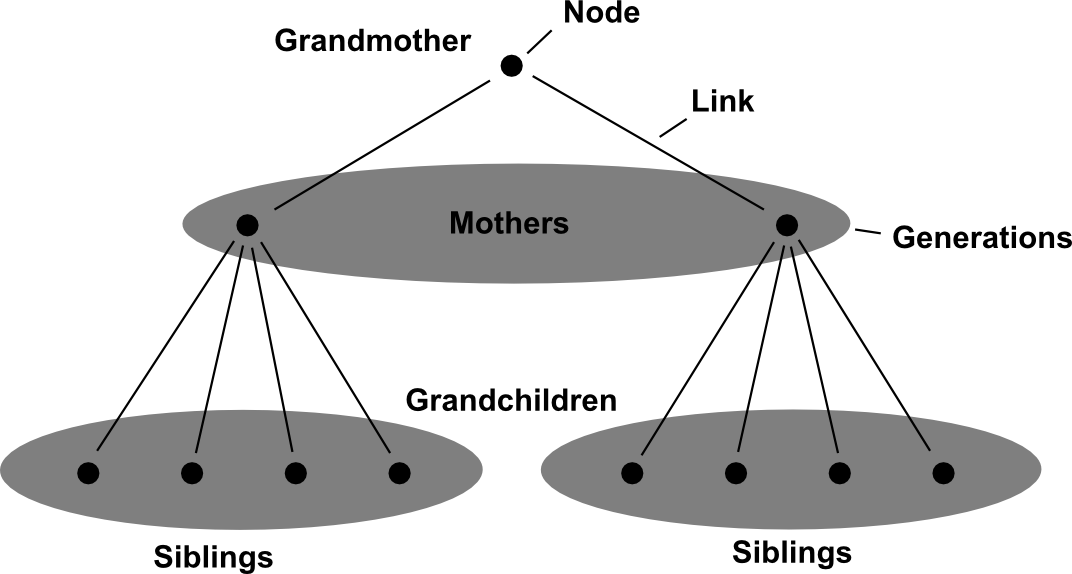
Diagrams

Projection theory is in Chapter 5


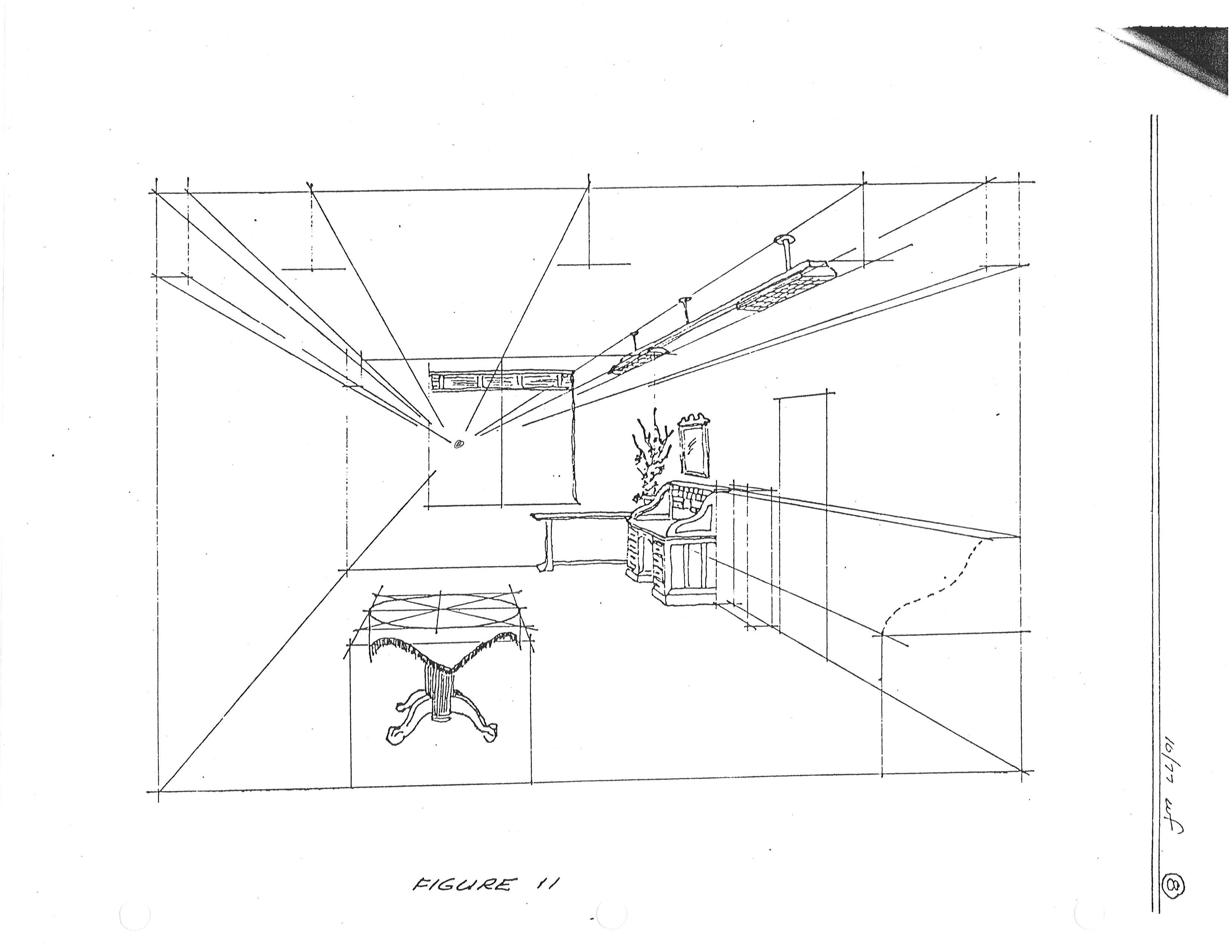
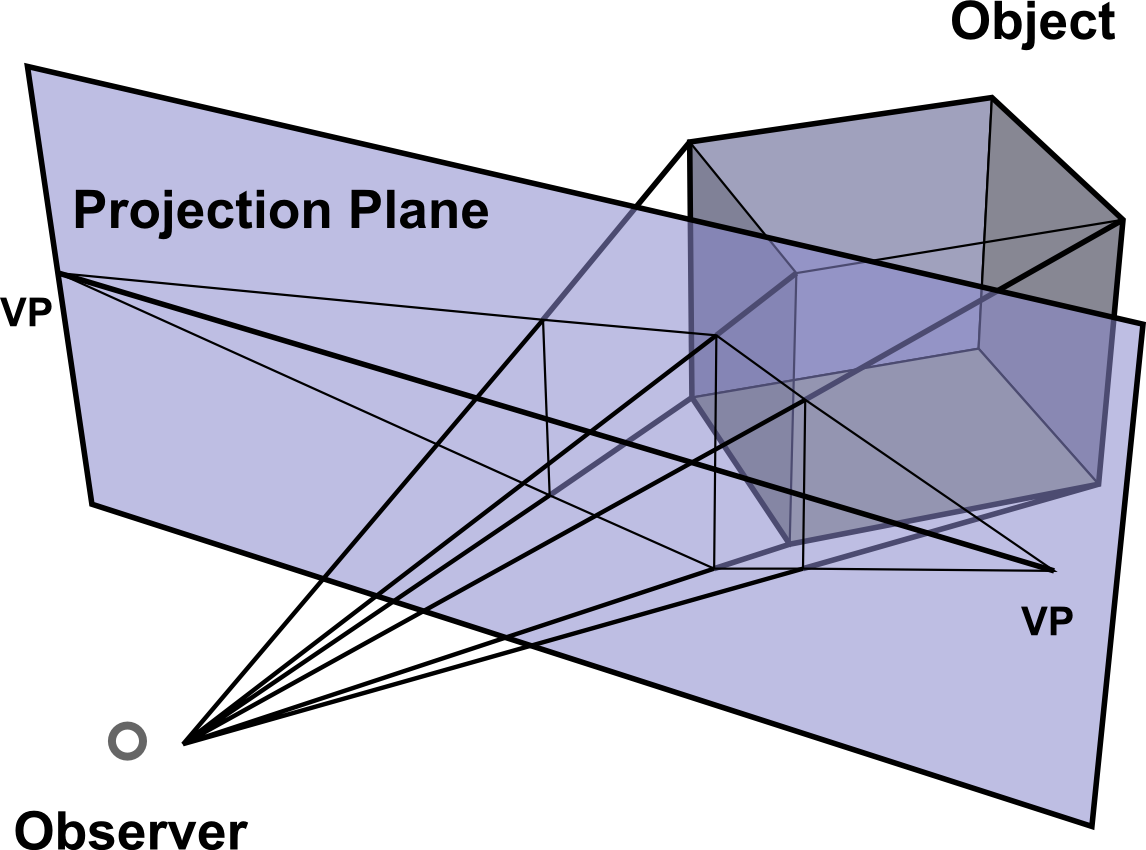

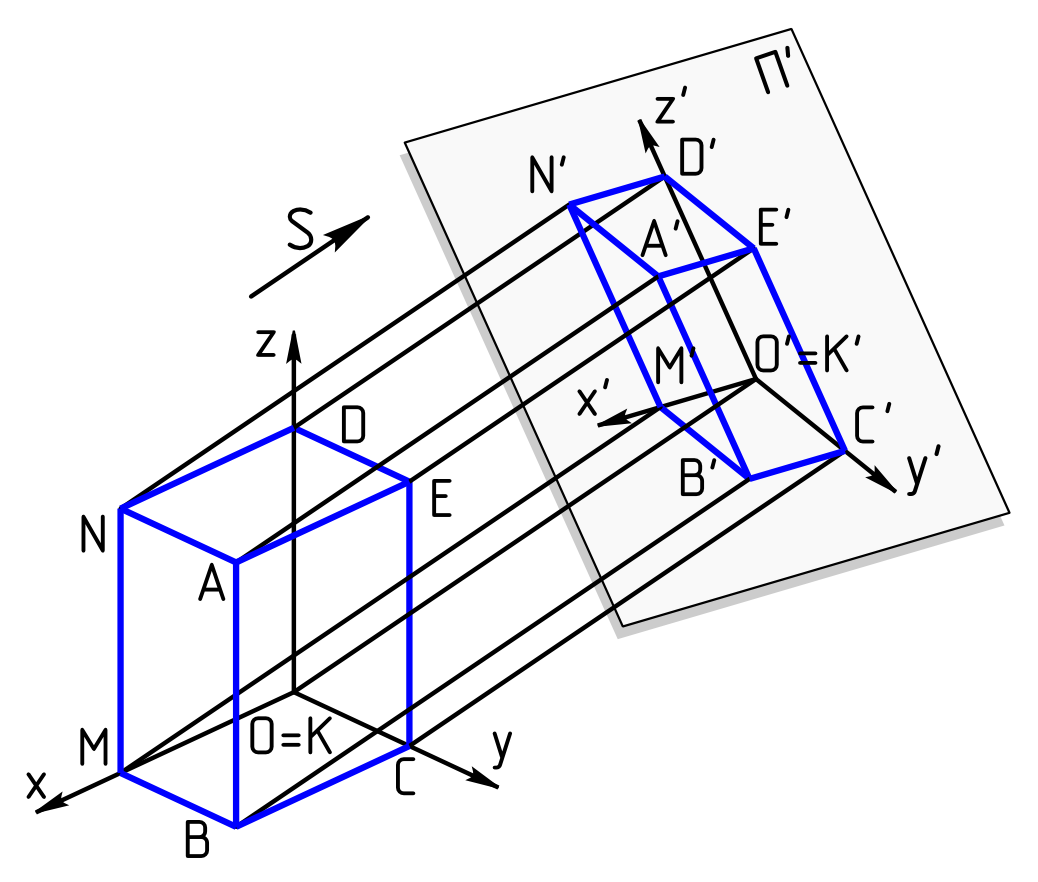
Parallel projection corresponds to a perspective projection with an infinite focal length (the distance from the image plane to the projection point)
Parallel project representation of a three dimensional object in two dimensions
To measure along axes.
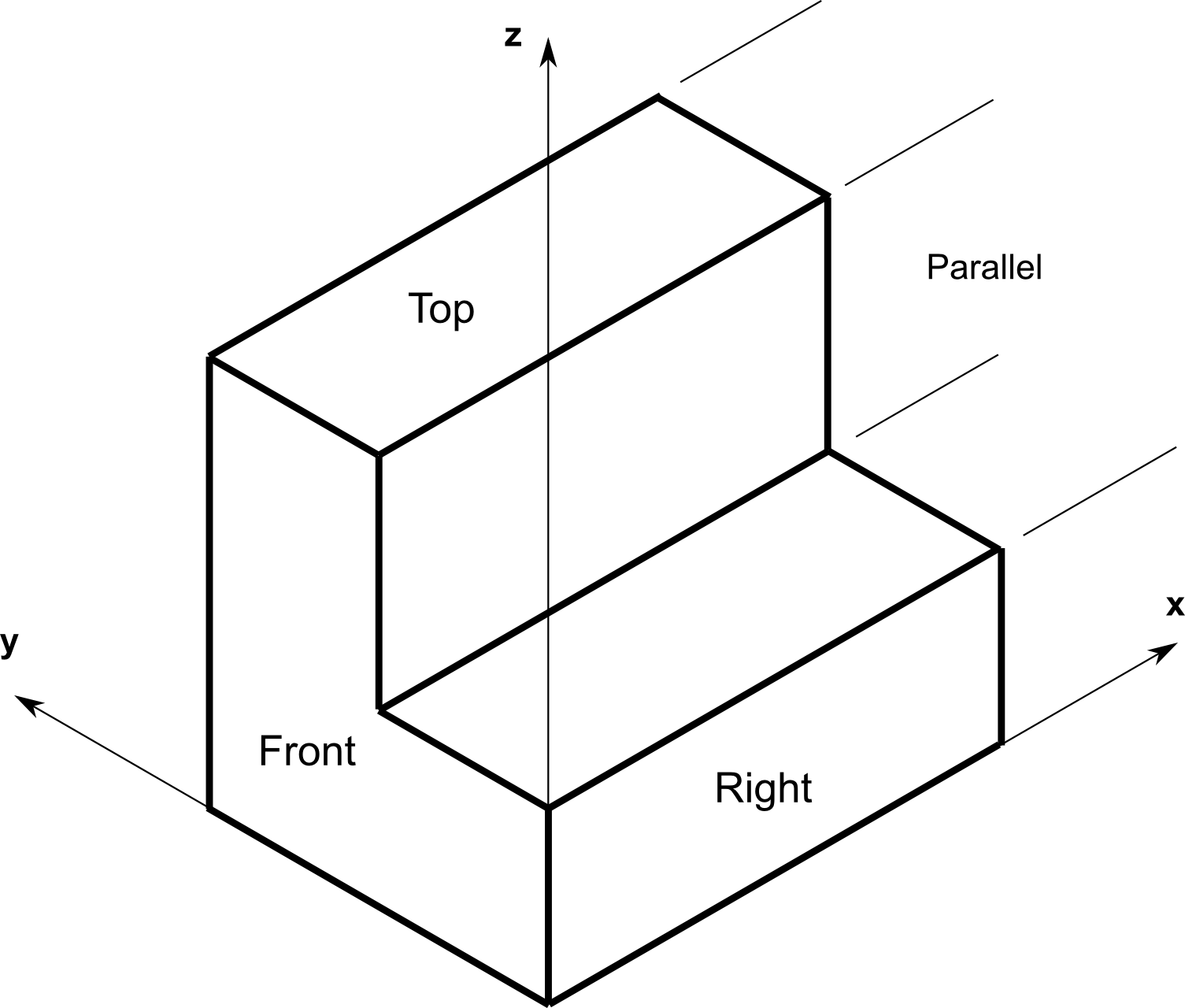
Up to 6 views of an object are projected onto planes perpendicular to the coordinate axes. The view positions follow one of two schemes: First Angle or Third Angle
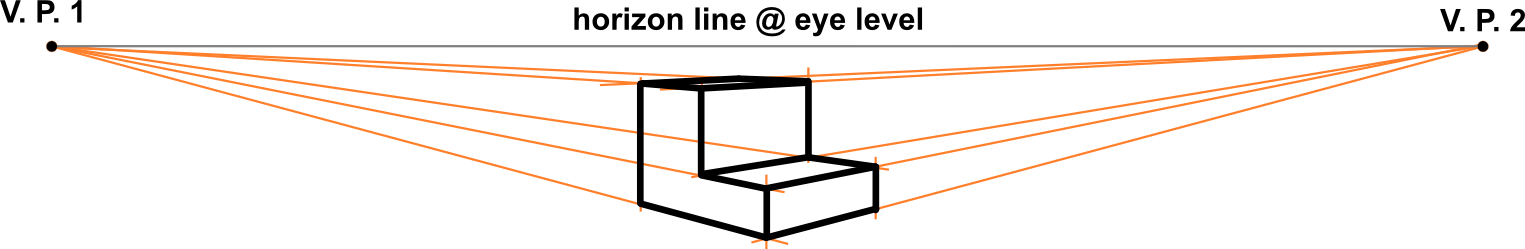
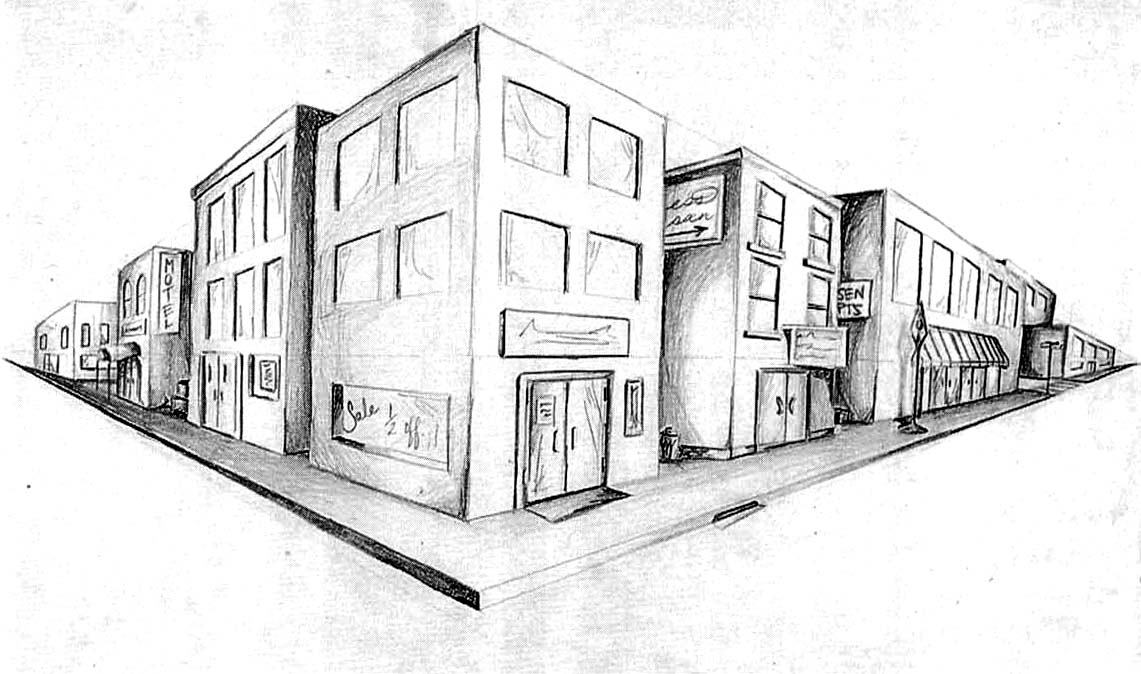
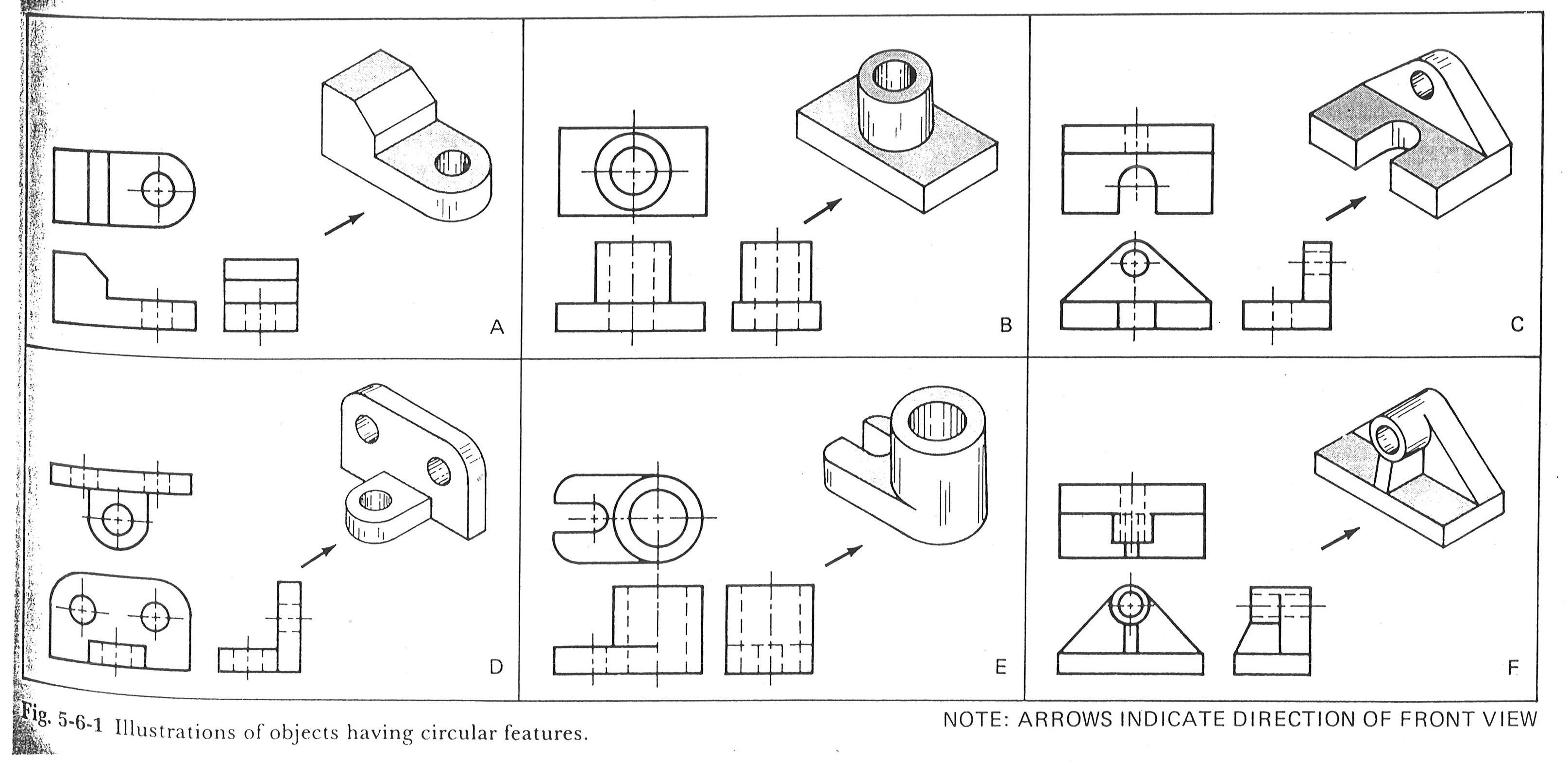
Image of object from skewed direction to reveal all axes
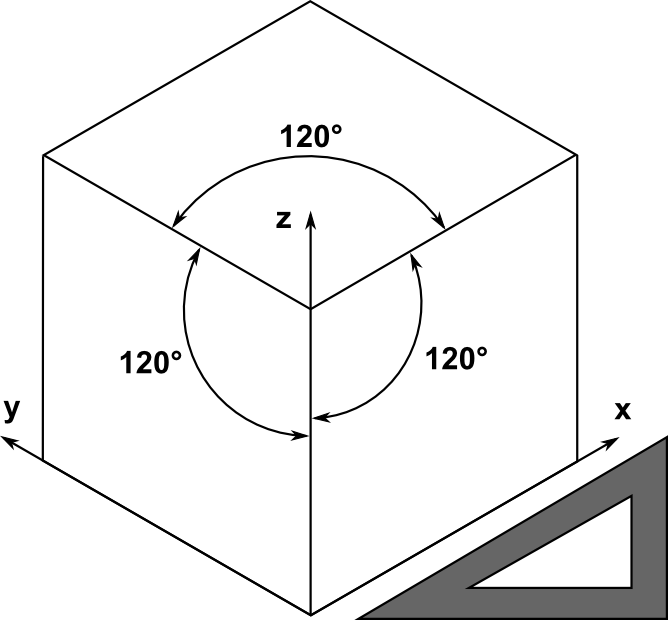
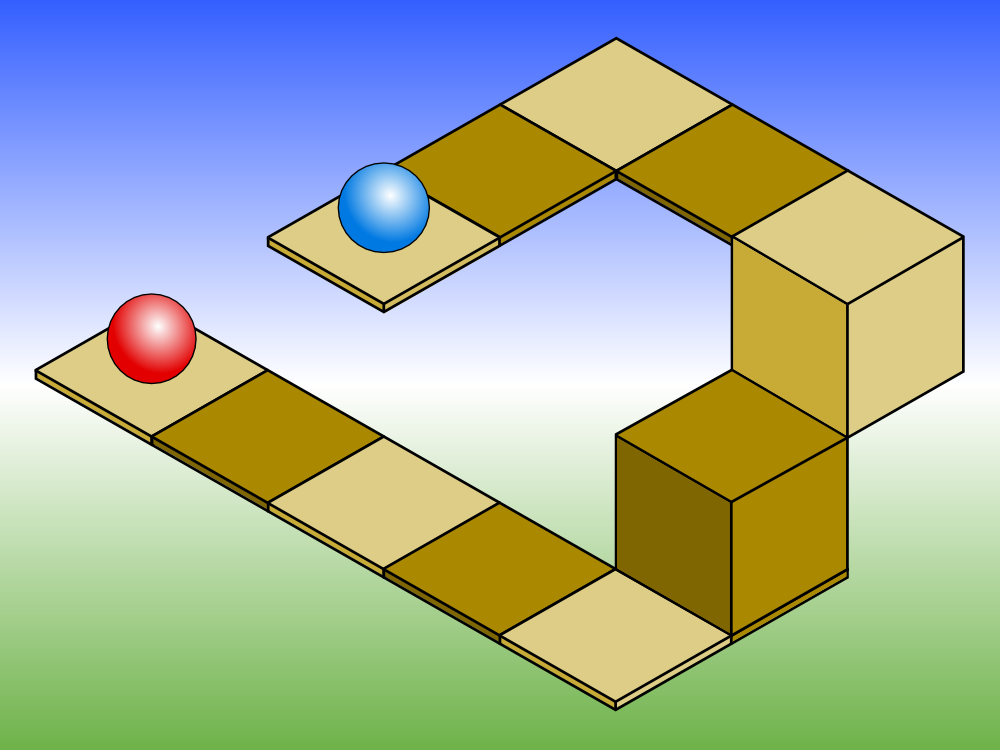
Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric
Type of parallel projection, more specifically a type of orthographic projection, used to create a pictorial drawing of an object, where the object is rotated along one or more of its axes relative to the plane of projection
All three axes are equally foreshortened and angled 120 degrees apart.
Lines are parallel.
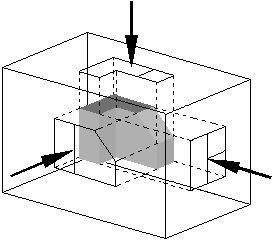
|
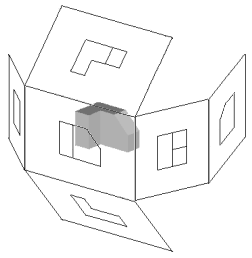
|
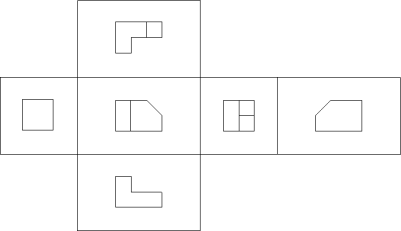
|

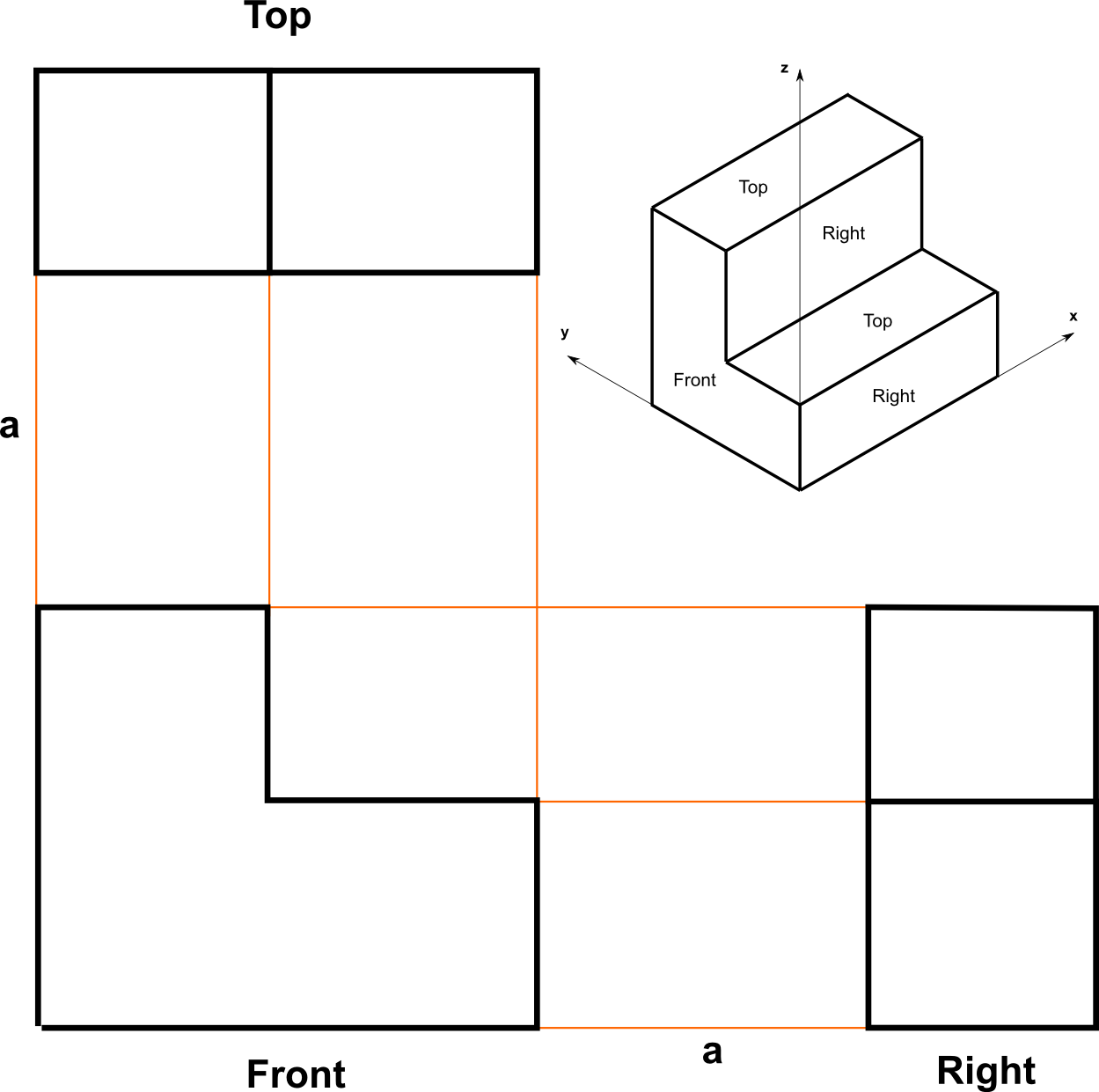
Projects an image by intersecting parallel rays (projectors) from the three-dimensional source object with the drawing surface (projection plane).
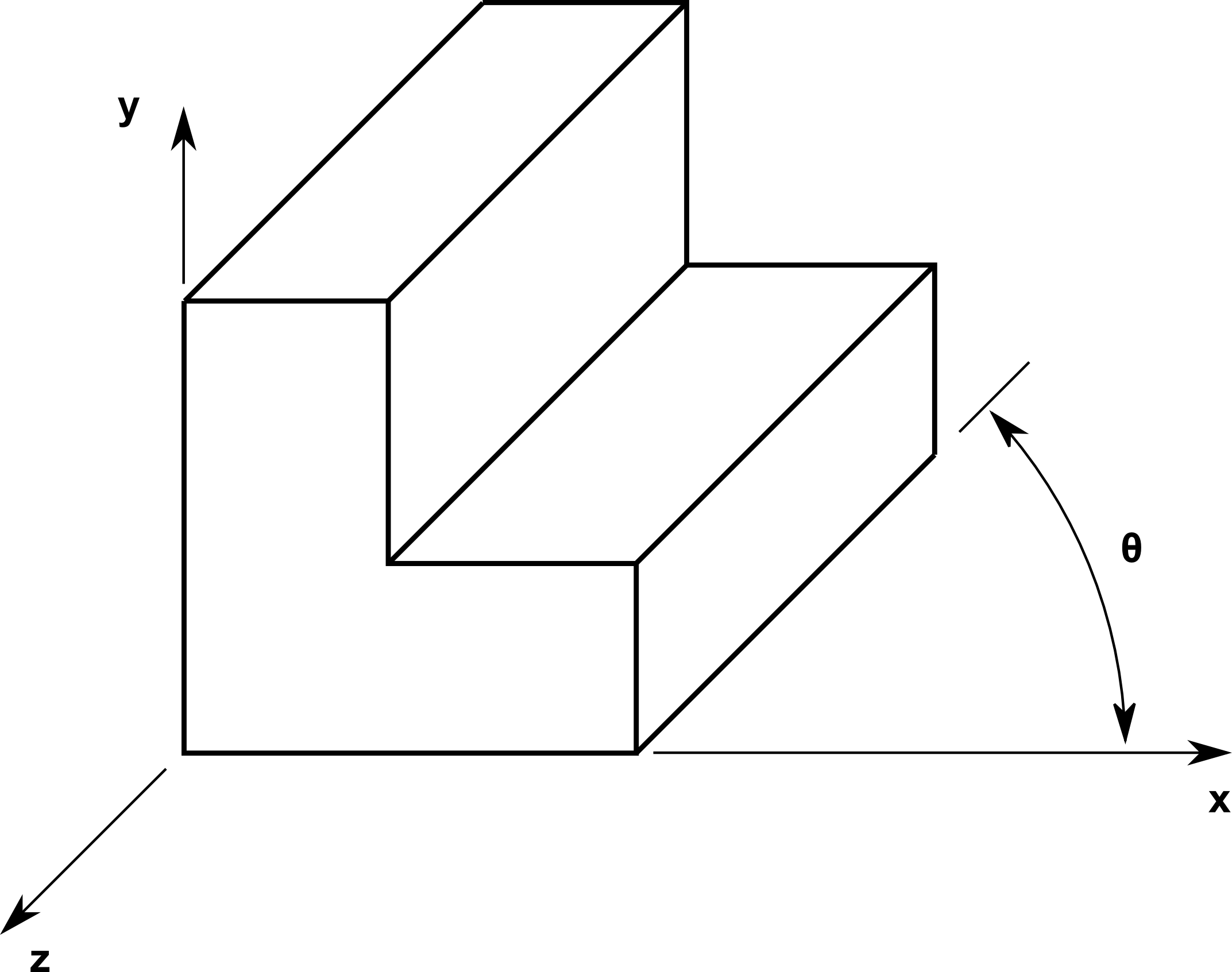
θ is typically 45 degrees
x-y scales are the same
z scale is between 0 and 1, usually 1/2
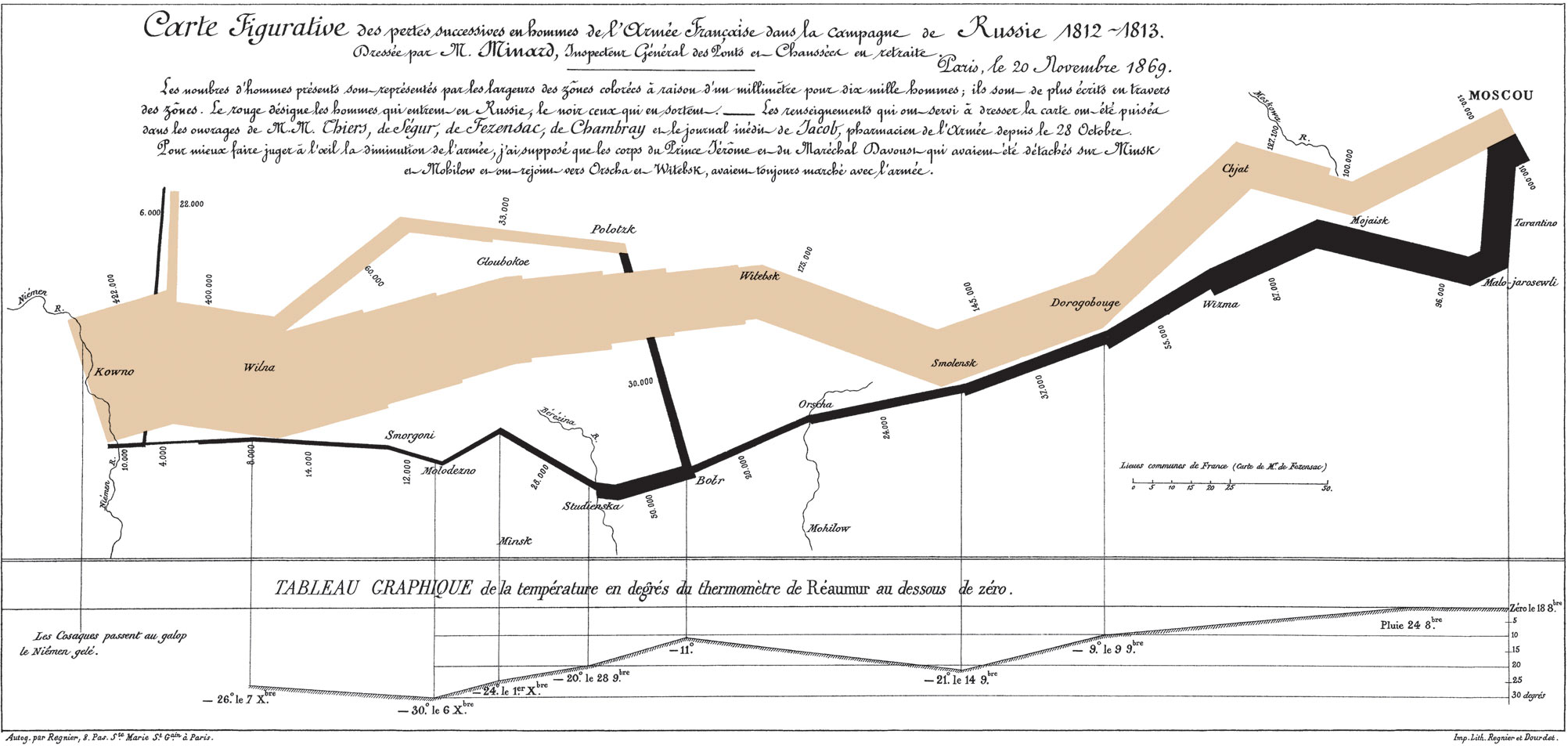
Ideas are captured in a visual format using symbols, words, lines, etc.
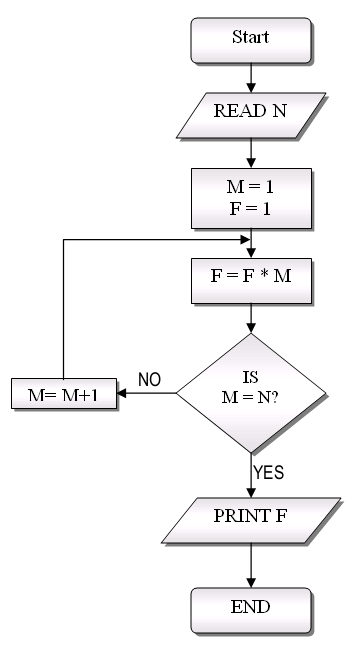
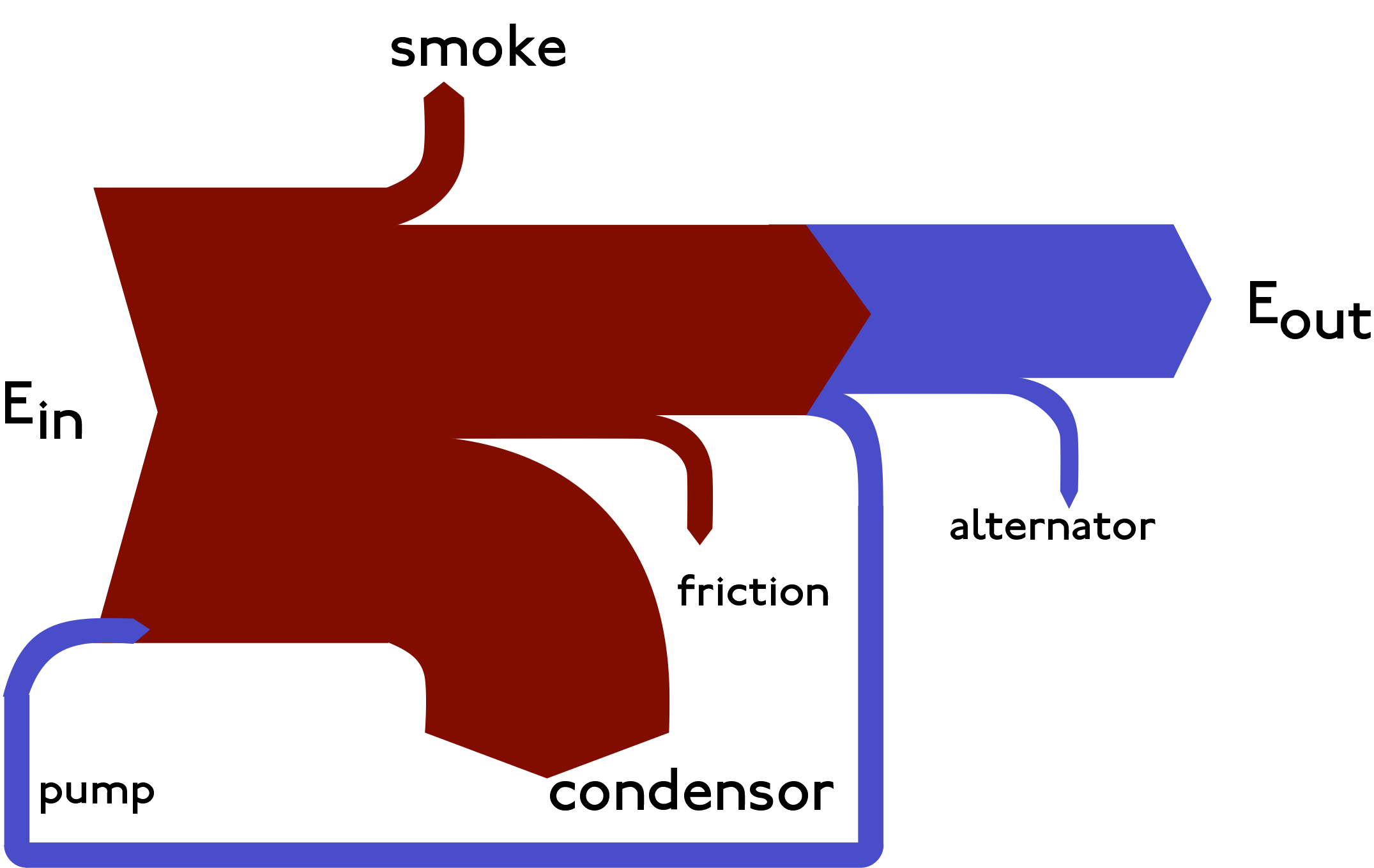
Represents an algorithm or process
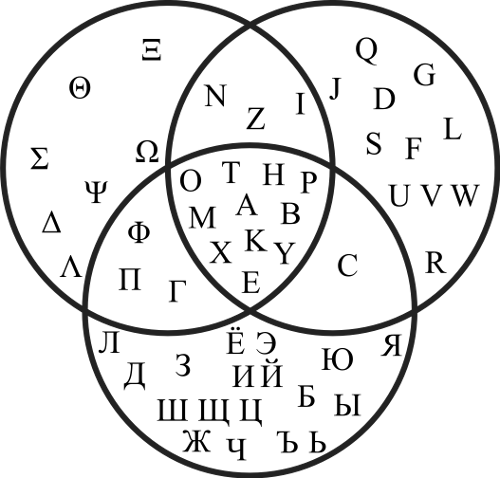
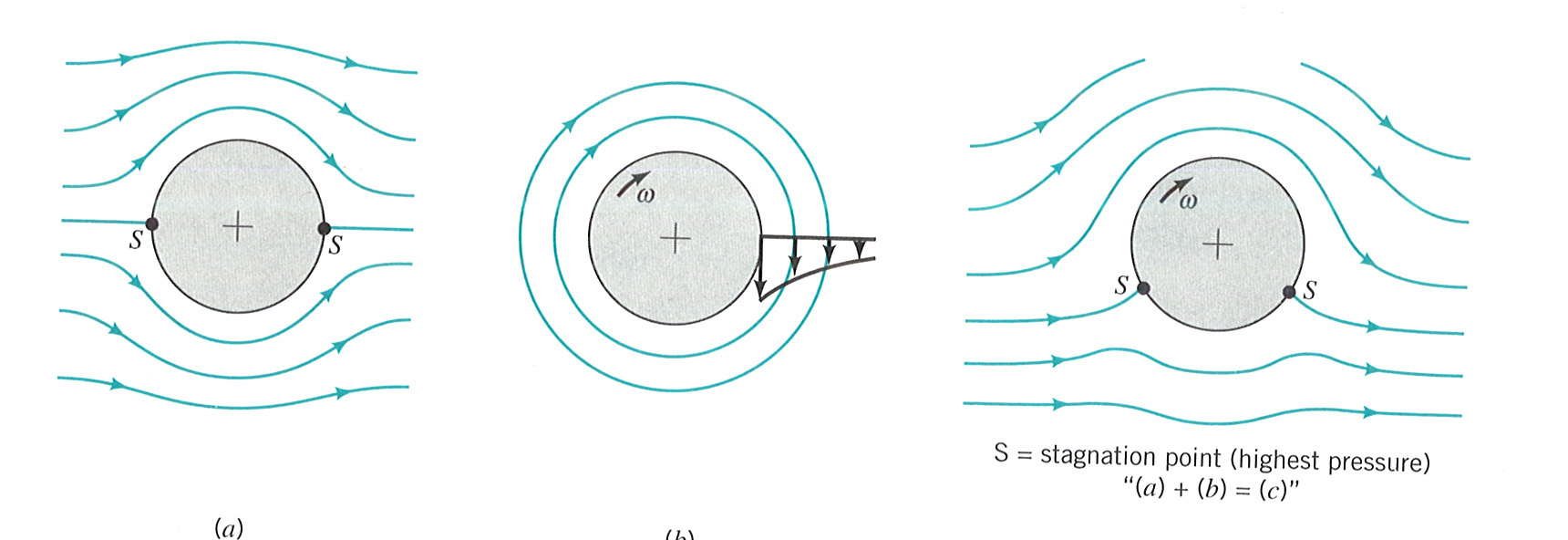
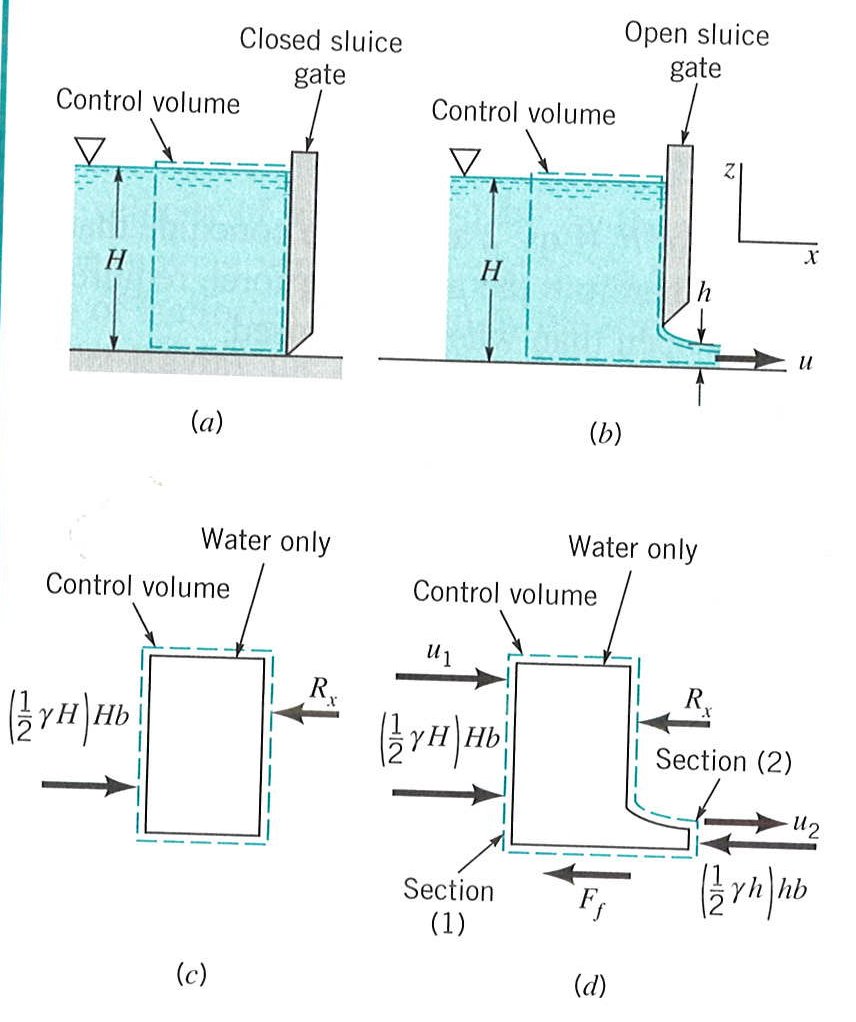
Show all possible logical relations between a finite collection of sets
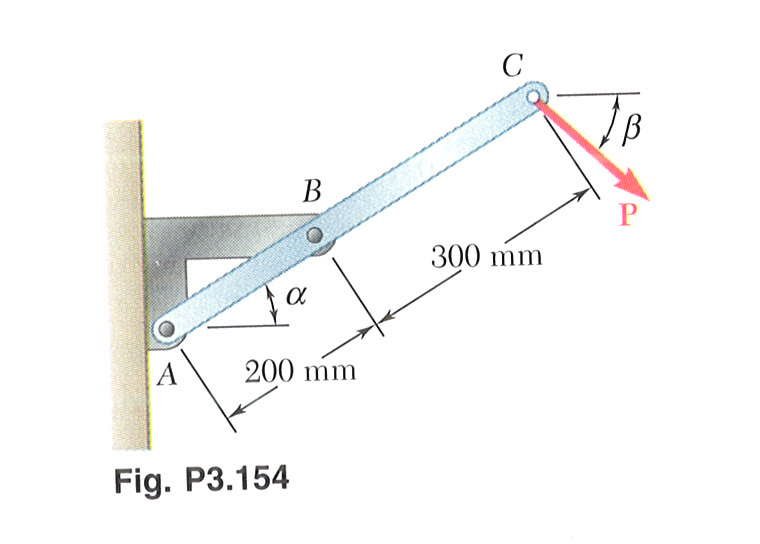 |
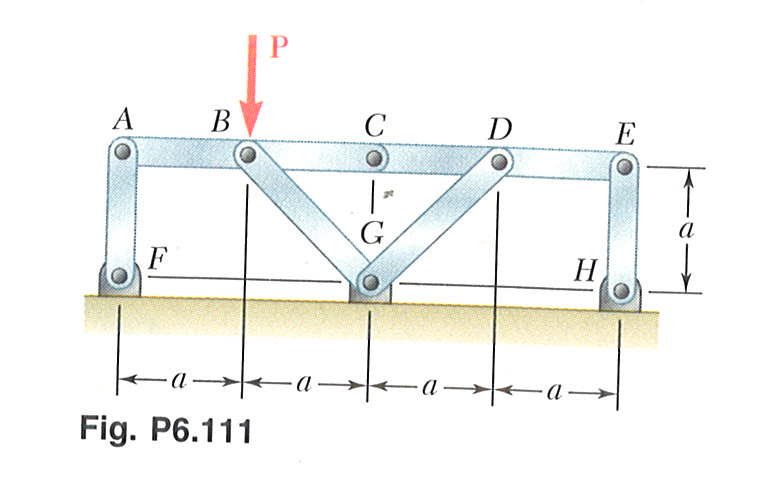 |
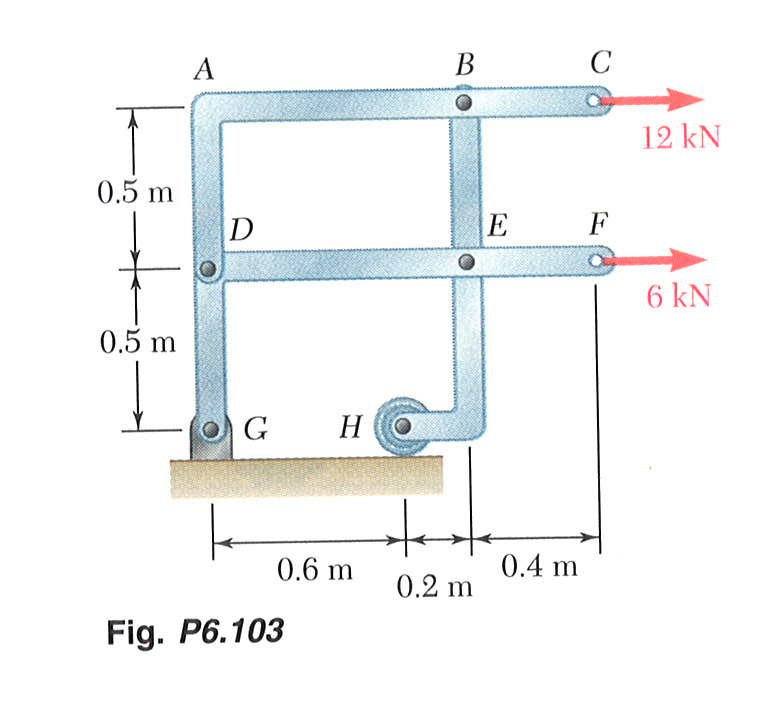 |
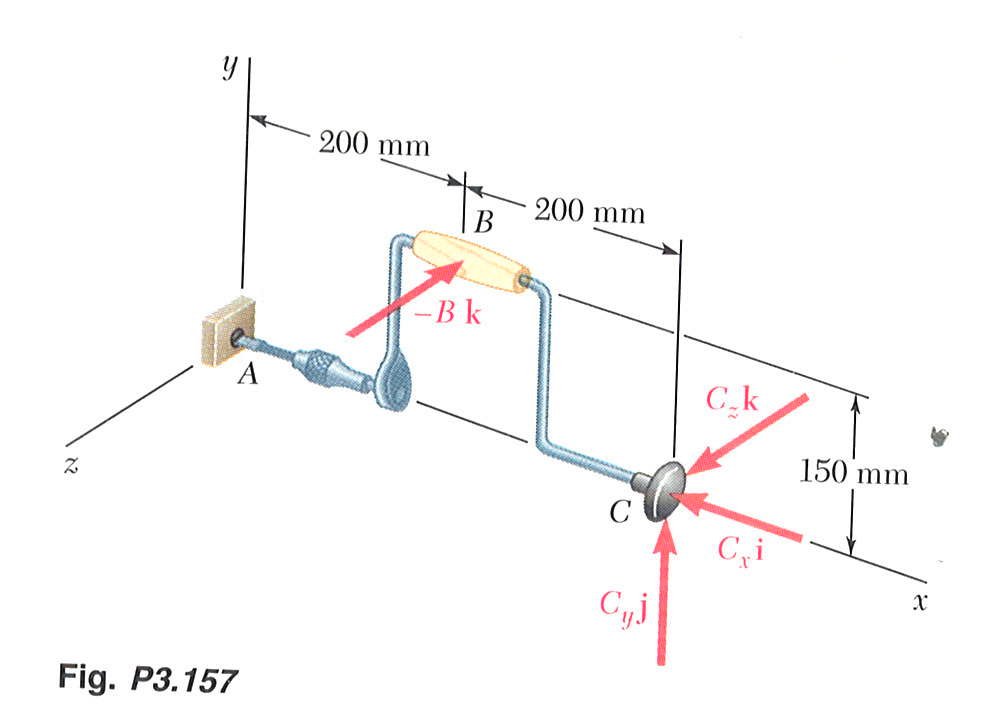 |
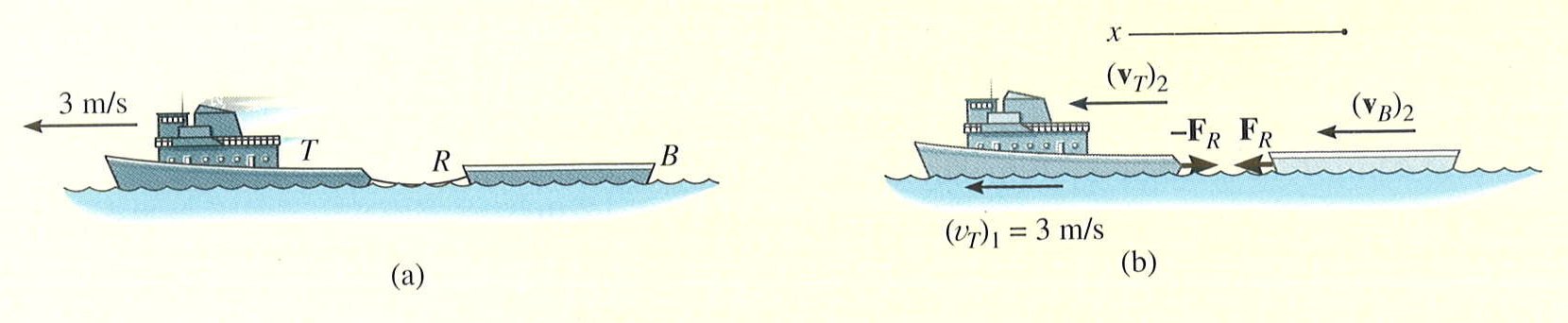
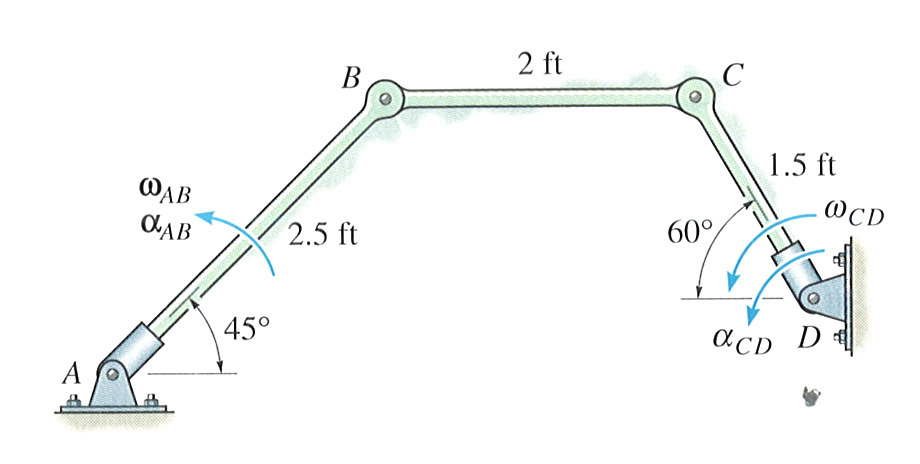 |
|
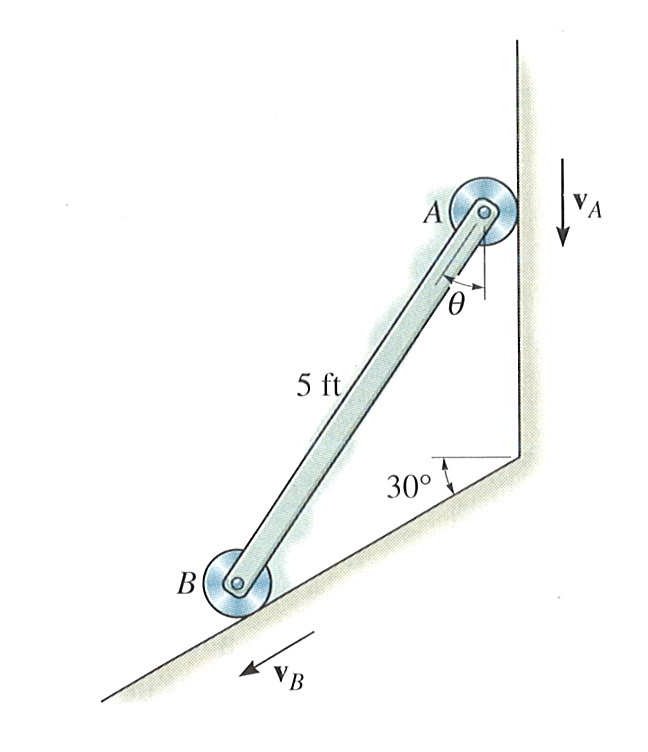 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
/
#